Design & Technology
‘We try to solve very complicated problems without letting people know how complicated the problem was.’ – Jonathan Ive
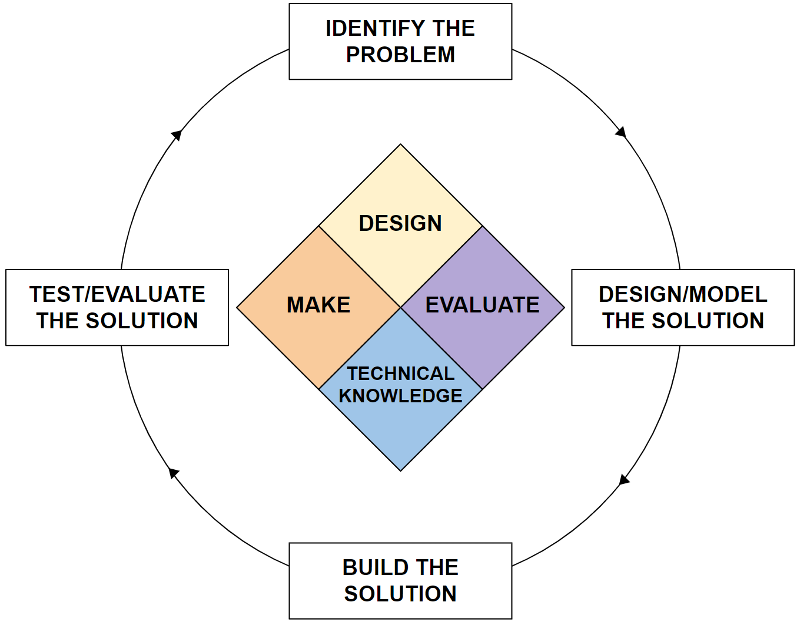
Our curriculum has been developed to enable students to engage in a diverse range of activities that foster problem solving skills, knowledge and application of commercial manufacturing techniques and technical expertise. Design and Technology offers a rigorous blend of both technical and practical competence that has real world application and relevance to user’s needs, wants and values. Our curriculum looks to provide our students with the fundamental knowledge of materials and processes, and an understanding of how these can be applied in a variety of contexts. Through the study of a range of key concepts, the curriculum promotes the use of technical knowledge, designing, modelling, manufacturing, testing and evaluation, to produce outcomes that are suitable for a wide range of users.
Design and Technology lessons aim to build a repertoire of knowledge that can be applied to solve real world problems in a variety of different contexts and disciplines. Students are taught how to perform practical skills confidently and become critical thinkers, enabling them to model, prototype, test and evaluate outcomes successfully. By combining both technical and practical expertise, students are supported in becoming independent and self-assured learners with a skillset that is transferable into both post-16 and industry pathways.